Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimizu, Yusuke*; Fujita, Takaaki*; Arimoto, Hideki*; Nakano, Tomohide; Hoshino, Kazuo; Hayashi, Nobuhiko
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 10(Sp.2), p.3403062_1 - 3403062_4, 2015/07
Kitazawa, Sin-iti; Maruyama, Toshiyuki; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Itami, Kiyoshi; Casal, N.*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 10(Sp.2), p.3402044_1 - 3402044_4, 2015/04
Hiratsuka, Junichi; Hanada, Masaya; Umeda, Naotaka; Kojima, Atsushi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Yoshida, Masafumi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 10(Sp.2), p.3405045_1 - 3405045_4, 2015/04
To produce high current density ( 200 A/m
200 A/m ), high-energy (
), high-energy ( 1 MeV) negative ion beams for long pulse duration time (1 hour) for International Thermo-nuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), the suppression of the direct interception of the negative ions with the grids has been carefully investigated with studying the deflection angle by aperture displacement technique. The non-linear dependence of the deflection angle appears at the aperture diameter of
1 MeV) negative ion beams for long pulse duration time (1 hour) for International Thermo-nuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), the suppression of the direct interception of the negative ions with the grids has been carefully investigated with studying the deflection angle by aperture displacement technique. The non-linear dependence of the deflection angle appears at the aperture diameter of  14 mm on a steering control grid (SCG). From this dependence, the aperture diameter and the offset distance of the SCG has been designed to be 16 mm and 0.7 mm, respectively and tested in a prototype accelerator for ITER. Each of the beamlets on the multiple apertures is properly steered with compensation of the deflection due to the residual magnetic field in the accelerator and the grid power loading was significantly reduced. It resulted in a 10% enhancement of the accelerated beam current.
14 mm on a steering control grid (SCG). From this dependence, the aperture diameter and the offset distance of the SCG has been designed to be 16 mm and 0.7 mm, respectively and tested in a prototype accelerator for ITER. Each of the beamlets on the multiple apertures is properly steered with compensation of the deflection due to the residual magnetic field in the accelerator and the grid power loading was significantly reduced. It resulted in a 10% enhancement of the accelerated beam current.
Maruyama, Takahito; Noguchi, Yuto; Takeda, Nobukazu; Kakudate, Satoshi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 10(Sp.2), p.3405010_1 - 3405010_4, 2015/02
Obana, Tetsuhiro*; Takahata, Kazuya*; Hamaguchi, Shinji*; Chikaraishi, Hirotaka*; Imagawa, Shinsaku*; Mito, Toshiyuki*; Kizu, Kaname; Murakami, Haruyuki; Natsume, Kyohei; Yoshida, Kiyoshi
no journal, ,
The central solenoid (CS) of JT-60SA is composed of 4 modules consisting of a quad-pancake and 6 octa-pancakes. In order to verify the process for the coil manufacturing and the fabrication jigs, the CS model coil was developed. The model coil is composed of one quad-pancake. The cold test of the model coil was conducted at the Nation Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS) test facility. The critical current, joint resistance, and pressure drop of the model coil were measured in the cold test. In addition, self-magnetic field of the model coil was measured using Hall sensors. The magnetic fields were varying slightly while holding coil current of 20 kA. The range of the time constant was from 17 sec to 571 sec, which was much longer than the time constant derived from the measurement using the short straight sample.
Yoshida, Maiko
no journal, ,
Mission of the JT-60SA project is to contribute to early realization of fusion energy by addressing key issues for ITER and DEMO. For the first plasma in March 2019, the manufacture of the main components has been going well on schedule both in the EU and Japan, and the JT-60SA project is now entering a new phase as it moves from manufacture of components to assembly. Parallel to the JT-60SA construction, the research plan for JT-60SA has been discussed in the fusion communities in Japan and Europe (more than 330 researchers from 40 institutes) to deepen and sharpen the research strategy for JT-60SA. Experiments in JT-60SA will be conducted over a wide range of operational regimes including ITER and DEMO relevant regimes. Both physics understanding of high performance plasmas (leading to plasma modeling) and developing plasma control systems are critical issues for ITER and DEMO that should be undertaken in JT-60SA.
Seto, Haruki; Breyiannis, G.*; Yagi, Masatoshi; Dudson, B.*; Xu, X.*
no journal, ,
In this study, we have developed a framework of the first principal simulation of the LH transition by 3field( ,
,  ,
, 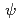 )-RMHD model in BOUT++ framework from those by 2field(
)-RMHD model in BOUT++ framework from those by 2field( ,
,  )-RMHD model reported by several research groups recently, where
)-RMHD model reported by several research groups recently, where  is the vorticity,
is the vorticity,  is the pressure and
is the pressure and 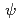 is the parallel vector potential. In these LH transition simulation framework, LH transition is described by the resistive ballooning mode (RBM) turbulence, the pressure profile determined by the dynamic balance of the energy transport and the poloidal damping effect (PDE) describing the radial force balance of the ion species including the poloidal rotation effect. In this presentation, we investigated the impact of the PDE on the RBM turbulence by nonlinear simulations with 3field-RMHD model and found that the PDE suppresses the RBM turbulence as a preliminary step for a first principal simulation of LH transition with 3field RMHD model.
is the parallel vector potential. In these LH transition simulation framework, LH transition is described by the resistive ballooning mode (RBM) turbulence, the pressure profile determined by the dynamic balance of the energy transport and the poloidal damping effect (PDE) describing the radial force balance of the ion species including the poloidal rotation effect. In this presentation, we investigated the impact of the PDE on the RBM turbulence by nonlinear simulations with 3field-RMHD model and found that the PDE suppresses the RBM turbulence as a preliminary step for a first principal simulation of LH transition with 3field RMHD model.
Miki, Kazuhiro; Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
From the perturbed gyrokinetic equation, we derive linear growth rates and real frequencies of the energetic-particle-induced geodesic acoustic mode (EGAM). Representing bump-on-tail distributions as the beam injection, we close the system together with the quasi-neutrality. Obtained dispersion relation, in which the finite-orbit-width (FOW) is taken, deduces the linear parameters depending on q-values, beam intensities, and plasma machine sizes. For experimentally-relevant parameters, the FOW effects are small, within several percent of the growth rates. The results are confirmed also in plasma size scan using the full-f gyrokinetic Eulerian code GT5D. We further introduce a slowing-down distribution function to compared with the DIII-D results and hybrid code simulation results. The comparison results in consistency.